| [ < ] | [ > ] | [ << ] | [ Up ] | [ >> ] | [Top] | [Contents] | [Index] | [ ? ] | [ Search: ] |
This section presents the main objects and files that are created when a Blender scene is exported.
The sectors, portals, lights and cameras are all exported in the ‘world’ file. This also means that they will be exported only if the ‘Export as a CS library’ option is not checked. See the section on the format of the Crystal Space map files for more information on the ‘world’ file.
The materials and mesh factories are exported in a Crystal Space ‘library’ file, either in the ‘factories’ directory or in the main ‘library’ file.
These objects are actually exported only if they are visible in the Blender scene (i.e. you haven't unchecked the Restrict visibility in the viewport option in the Blender outliner).
The maps in Crystal Space can be split in several sectors linked by portals. The concept of sectors corresponds to the one of the Blender scenes, but Blender has no matching concept for the portals.
Each scene in Blender will therefore be exported as a different sector in the Crystal Space ‘world’ file. For the creation of the portals that will link together the sectors, please have a look at the dedicated page.
All visible cameras in Blender will be exported as camera positions (i.e.
iCameraPosition objects) in the Crystal Space ‘world’ file. The
name of the camera objects is important since they are exported in the
alphabetical order of their name, with the first camera serving as the starting
position in the Crystal Space scene.
All visible lamps in Blender will be exported as lights in Crystal Space. The following types are supported:
All others are exported as point lights and the other lamp properties are ignored.
A Crystal Space panel is accessible in the ‘Object Data’ context of the ‘Properties’ window. A single option, ‘No shadows’, is available: it determines whether or not this lamp can cast shadows.
All the mesh objects that are visible in the Blender scene will be exported, either as a static mesh or an animated mesh. For each different mesh, a file containing the definition of the mesh factory will be generated in the ‘factories’ directory. Each instance of the mesh will get an entry in the ‘world’ file.
You can parent objects in Blender and they will be exported as similar object hierachies in Crystal Space.
All the textures that are used by any of the exported meshes will be exported in the ‘textures’ directory.
Only the main material properties will be exported, such as the diffuse map, the specular map and specular color, the normal map, and the displacement (parallax) map.
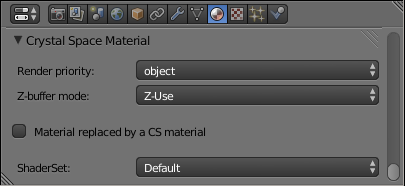
In addition to these Blender material properties, a dedicated panel is accessible in the ‘Material’ context of the ‘Properties’ window:

Some additional options are displayed if ‘Shaderset’ is set to ‘water_plane’.
Note the last two options in the panel, ‘Render priority’ and ‘Z-buffer mode’, that allows to define the rendering behavior of the submeshes associated to the current material. For materials using transparent textures, you would typically use a render priority of e.g. ‘transp’, and the Z-buffer mode ‘Z-Test’.
Most other Blender material properties are not exported, such as the mirror properties, the subsurface scattering, the shadows, etc. Also, materials using the node composition system of Blender are not supported at all.
| [ < ] | [ > ] | [ << ] | [ Up ] | [ >> ] | [Top] | [Contents] | [Index] | [ ? ] |
This document was generated using texi2html 1.76.